Traditional Uses and Pharmacology Study of Piper betle L. :A Systematic Review
Keywords:
Piper betle L., Pharmacology, Antibacterial, Bioactive Compounds, Literature reviewAbstract
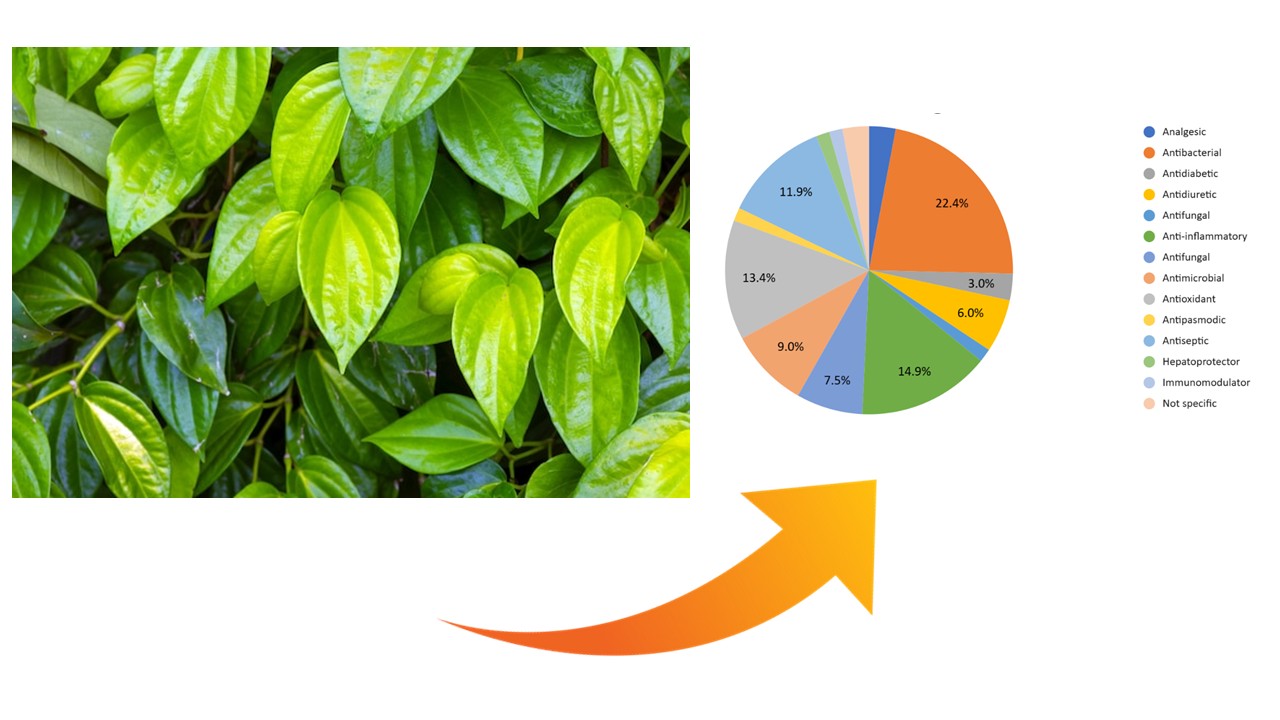
Betel leaf (Piper betle L.) is a plant that has been widely used for medicinal purposes. Parts of the betel plant, such as the roots, seeds, and leaves, have potential for medicinal use, but the leaves are most commonly used. Empirically, betel leaves have been used by the community as an antibacterial agent. There are many studies and research that have reported the antibacterial activity of betel leaves. Its diverse bioactive compounds, such as flavonoids, phenols, and essential oils, provide a broad pharmacological potential. This study aims to identify the pharmacological effects of betel leaves based on a systematic literature review (PRISMA). Literature searches were conducted through scientific databases such as Google Scholar using relevant keywords. Thirty articles selected were published within a certain period and met the inclusion criteria. The results of the review showed that betel leaves have various pharmacological activities, including antibacterial, antifungal, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and analgesic. Flavonoids and phenols play an important role in antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities, while essential oils contribute to antimicrobial activity. This literature review highlights that green betel leaf (Piper betle L.) possesses significant pharmacological effects, including antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory activities, and other therapeutic potentials, making it a promising natural candidate for herbal medicine development.